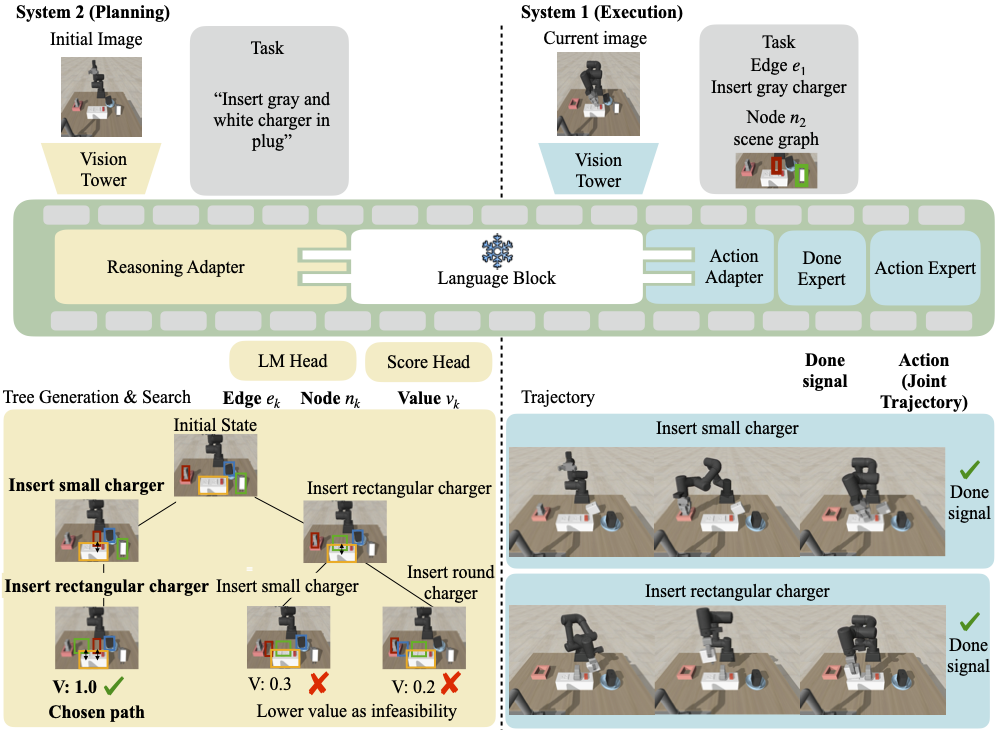
- Train a vision–language–action planner on mixed teleoperation data (success + failure).
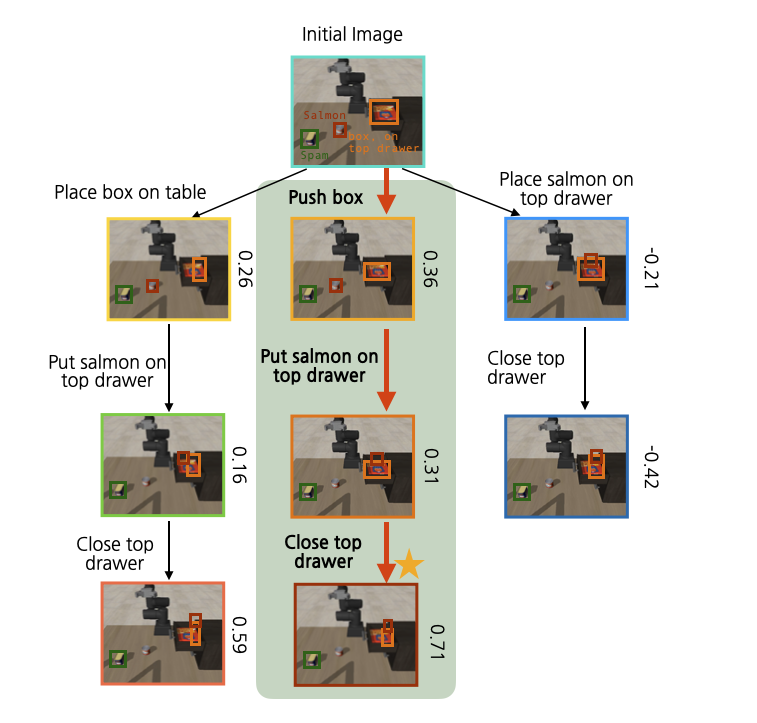
- System 2 builds a scene graph and uses a value head with tree search to select feasible subgoals.
- System 1 executes the chosen subgoal sequence as continuous actions with a learned done signal.
Hierarchical Vision Language Action Model Using Success and Failure Demonstrations
Abstract
Prior Vision–Language–Action (VLA) models are typically trained on teleoperated successful demonstrations, while discarding numerous failed attempts that occur naturally during data collection. However, these failures encode where and how policies can be fragile, information that can be exploited to improve robustness. We address this problem by leveraging mixed-quality datasets to learn failure-aware reasoning at plan- ning time. We introduce VINE, a hierarchical vision-language- action model that separates high-level reasoning (System 2) from low-level control (System 1) under a hierarchical reinforcement learning formalism, making failures usable as a structured learning signal rather than noisy supervision. System 2 performs feasibility-guided tree search over a 2D scene-graph abstraction: it proposes subgoal transitions, predicts success probabilities from both successes and failures, and prunes brittle branches before execution, effectively casting plan evaluation as feasibility scoring. The selected subgoal sequence is then passed to System 1, which executes low-level actions without modifying the agent’s core skills. Trained entirely from offline teleoperation data, VINE integrates negative experience directly into the decision loop. Across challenging manipulation tasks, this approach con- sistently improves success rates and robustness, demonstrating that failure data is an essential resource for converting the broad competence of VLAs into robust execution.
Proposed method
Result Videos
Put towel in cabinet and close it (unseen color of towel)
Generated Tree
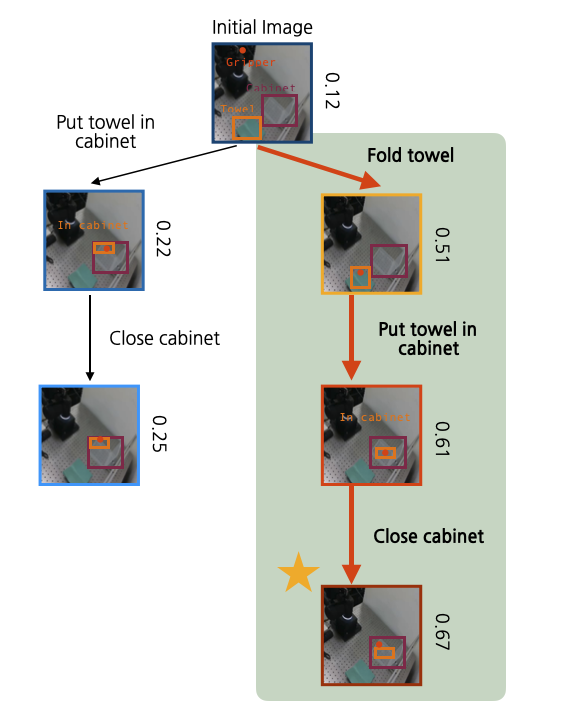
Execution
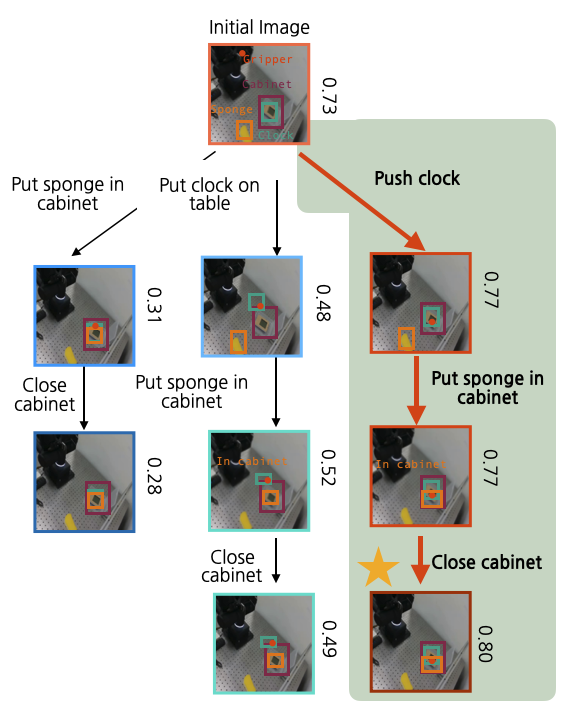
Put sponge in cabinet and close it (unseen color of sponge)
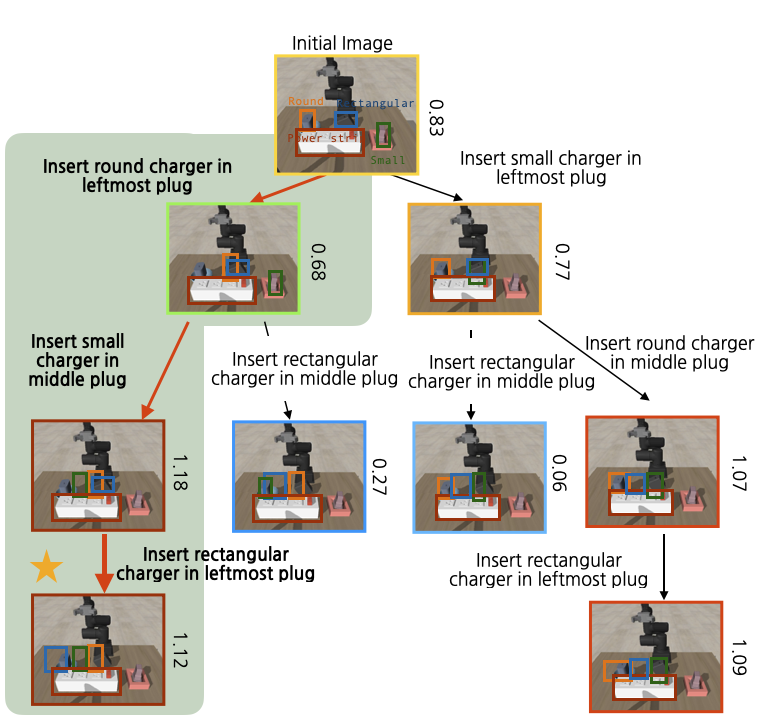
Insert all chargers in power strip (unseen color of chargers)
Put spam in top drawer and close it (unseen distractor)
Comparison Videos
Put sponge in cabinet and close it
pi_0
Seen
❌
VINE (Ours)
Seen
✅
pi_0
Unseen Color
❌
VINE (Ours)
Unseen Color
✅
Put towel in cabinet and close it
Seen
✅
Seen
✅
Unseen Color
❌
Unseen Color
✅
Put salmon can on top drawer and close it.
pi_0
Seen
❌
GR00T N1.5
Seen
❌
Gemini-2.5 as System 2
Seen
❌
VINE (Ours)
Seen
✅
Unseen distractor
❌
Unseen distractor
❌
Unseen distractor
❌
Unseen distractor
✅
Put spam can on top drawer and close it.
Seen
❌
Seen
✅
Seen
✅
Seen
✅
Unseen color of box
⚠️
Unseen color of box
⚠️
Unseen color of box
❌
Unseen color of box
✅
Unseen color of can
✅
Unseen color of can
✅
Unseen color of can
❌
Unseen color of can
✅
Insert all chargers in power strip.
pi_0
Seen
⚠️
GR00T N1.5
Seen
❌
Gemini as System 2
Seen
✅
VINE (Ours)
Seen
✅
Unseen shape of chargers
⚠️
Unseen shape of chargers
⚠️
Unseen shape of chargers
❌
Unseen shape of chargers
✅
Unseen color of chargers
⚠️
Unseen color of chargers
❌
Unseen color of chargers
❌
Unseen color of chargers
✅
Insert small and rectangular charger in power strip.
Seen
✅
Seen
❌
Seen
✅
Seen
✅
Unseen placement of chargers
❌
Unseen placement of chargers
✅
Unseen placement of chargers
❌
Unseen placement of chargers
✅
Dataset Samples
Teleoperated demonstrations collected in both simulation and real-world setups using a leader-arm interface. The actual trained demonstrations are shown bellow.
Videos with red border indicate failure demonstrations, while those with green border indicate successful ones.
Real-World Environment Dataset (Teleoperated)
Drawer Packing Environment Dataset (Teleoperated)
Plug Insertion Environment Dataset (Teleoperated)
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Taerim Yoon for providing valuable feedback on earlier versions of the manuscript. We also thank Irving Fang for providing the base models and implementation guidance for the Simpler environment experiments.
BibTeX
@article{park2025hierarchicalvisionlanguageaction,
title={Hierarchical Vision Language Action Model Using Success and Failure Demonstrations},
author={Jeongeun Park and Jihwan Yoon and Byungwoo Jeon and Juhan Park and Jinwoo Shin and Namhoon Cho and Kyungjae Lee and Sangdoo Yun and Sungjoon Choi},
year={2025},
eprint={2512.03913},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.RO},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.03913},
}